[edsanimate_start entry_animation_type= “bounceIn” entry_delay= “0.5” entry_duration= “0.5” entry_timing= “ease-out” exit_animation_type= “” exit_delay= “” exit_duration= “” exit_timing= “” animation_repeat= “1” keep= “yes” animate_on= “load” scroll_offset= “” custom_css_class= “”] [edsanimate_end]
[edsanimate_end]
 [edsanimate_end]
[edsanimate_end]
Clinical sharps generated within a hospital environment are disposed of in a number of different ways, depending on whether or not the sharps are contaminated. If clinical sharps are not disposed of correctly, then hazards and risks will emerge. The main hazard is, of course, the sharps themselves. Risks associated with sharps injuries are minor lacerations, puncture wounds and acquiring a blood borne virus.
Again, different colour codes are used to segregate sharps. Sharps bins are distinguished by different coloured lids: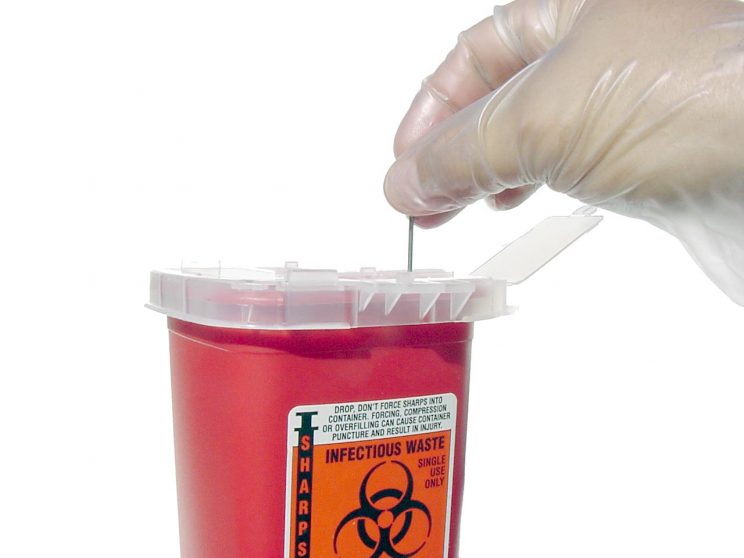
- Purple
- Orange
- Yellow
- White
Purple lid
- Ampoules containing cytotoxic or cytostatic medicines
- Sharps and syringes containing cytotoxic and cytostatic medicines
- Intravenous giving sets containing cytotoxic or cytostatic medicines
Orange lid
- Ampoules (fully discharged except for cytotoxic and cytostatic medicines)
- Catheters/cannulae, intravenous (insertion device only)
- Fully discharged intravenous giving set (except for cytotoxic and cytostatic medicines) if spike exposed
- Needles (with or without syringe attached)
- Sharps from phlebotomy
Yellow Lid
- Ampoules – still containing medicines (except cytostatic or cytotoxic)
- Partially discharged sharps (except cytostatic or cytotoxic)
- Syringe body used for medicines (partly discharged, except cytostatic or cytotoxic)
- Intravenous giving set containing residual medication (except cytostatic and cytotoxic drugs)
All amalgam waste (dental) should be disposed of in a white (rigid) waste container.
